Q: What are qualitative methods in research?
A:
- 📊 Qualitative methods in research involve collecting and analyzing non-numerical data to understand phenomena from a subjective perspective.
- 📈 They focus on exploring meanings, experiences, perceptions, and social contexts through methods such as interviews, observations, and content analysis.
Q: Why are qualitative methods important in research?
A:
- 🎯 Qualitative methods provide in-depth insights into complex social phenomena, allowing researchers to explore diverse perspectives, beliefs, and experiences.
- 📊 They complement quantitative approaches by capturing rich, nuanced data that quantitative methods may overlook.
- 💡 Qualitative methods are valuable for generating hypotheses, exploring new topics, and informing the development of theories or models.
Q: What are the common qualitative research methods?
A:
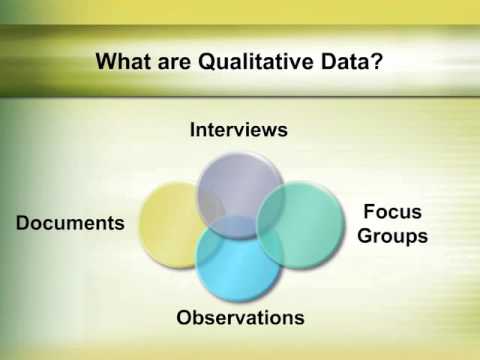
- 📉 Interviews: Conducting semi-structured or unstructured interviews to explore participants’ perspectives, experiences, and narratives.
- 📊 Observation: Immersing in the research setting to observe and document behaviors, interactions, and social dynamics.
- 📈 Focus Groups: Facilitating group discussions to elicit collective insights, opinions, and shared experiences on a specific topic.
- 💬 Content Analysis: Analyzing textual or visual data, such as documents, transcripts, or images, to identify themes, patterns, or discourses.
- 🎨 Ethnography: Engaging in long-term immersion in a cultural or social setting to understand the cultural practices, norms, and values of a group.
Q: How are qualitative methods applied in research?
A:
- 📊 Data Collection: Collecting qualitative data through methods such as interviews, observations, or document analysis, often using purposive sampling to select participants or sources.
- 📈 Data Analysis: Analyzing qualitative data using techniques such as thematic analysis, narrative analysis, or grounded theory to identify patterns, themes, or meanings.
- 💡 Interpretation: Interpreting the findings in relation to the research questions, theoretical frameworks, or broader socio-cultural contexts, often using reflexivity to acknowledge the researcher’s subjectivity.
- 📉 Triangulation: Validating qualitative findings through triangulation with multiple data sources, methods, or researchers to enhance credibility and trustworthiness.
Q: What are the strengths of qualitative methods?
A:
- 🎯 Richness and Depth: Qualitative methods allow for a rich exploration of complex phenomena, capturing nuances, contradictions, and contextual factors.
- 📊 Flexibility: Qualitative research is flexible and adaptable, allowing researchers to explore emergent themes or unexpected findings.
- 💡 Participant Perspectives: Qualitative methods prioritize participants’ voices and perspectives, providing insights into lived experiences and subjective meanings.
- 📈 Theory Development: Qualitative research contributes to theory development by generating hypotheses, conceptual frameworks, or theoretical constructs grounded in empirical data.
Q: What are the limitations of qualitative methods?
A:
- 📉 Subjectivity: Qualitative research is inherently subjective, as it relies on the researcher’s interpretation of data, potentially leading to bias or researcher influence.
- 📊 Generalizability: Findings from qualitative research may not be generalizable to broader populations or contexts due to the small sample sizes and context-specific nature of the data.
- 💡 Time and Resources: Qualitative research can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, requiring extensive data collection, transcription, and analysis.
- 📈 Validity and Reliability: Ensuring the validity and reliability of qualitative findings can be challenging, as they depend on the rigor of data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
In summary, qualitative methods offer valuable insights into complex social phenomena, providing rich, contextually situated data that deepen our understanding of human experiences, behaviors, and interactions. While qualitative research has its strengths and limitations, it is an essential approach for exploring subjective meanings, social contexts, and lived realities in diverse research domains.
-

Qualitative research methodology I qualitative research methods an overview
-

Qualitative research methods
-
Overview of Qualitative Research Methods
-

QUALITATIVE Research Design: Everything You Need To Know (With Examples)
-

Fundamentals of Qualitative Research Methods: What is Qualitative Research (Module 1)
-

Quantitative vs. Qualitative Research: The Differences Explained | Scribbr 🎓
