Q: What are the different methods used in qualitative research in management?
A:
- 📊 Interviews: Conducting structured, semi-structured, or unstructured interviews with individuals to gather insights into their experiences, perceptions, and viewpoints related to management issues.
- 📈 Observations: Engaging in participant observation or non-participant observation to directly observe organizational practices, behaviors, and interactions within management contexts.
- 💡 Focus Groups: Facilitating group discussions with a selected sample of participants to explore shared perspectives, opinions, and attitudes toward specific management topics.
- 🎯 Case Studies: Conducting in-depth examinations of real-life organizational cases or scenarios to understand complex management phenomena within their contextual environments.
- 📉 Content Analysis: Analyzing textual or visual data, such as documents, reports, or social media content, to identify themes, patterns, or trends relevant to management research questions.
- 📊 Ethnography: Immersing in the organizational setting over an extended period to gain a deep understanding of its culture, norms, and practices from an insider’s perspective.
- 📈 Grounded Theory: Inductively developing theories or conceptual frameworks grounded in empirical data collected through systematic observation and analysis of management phenomena.
- 💬 Narrative Analysis: Examining personal or organizational narratives, stories, or anecdotes to uncover underlying meanings, themes, and structures relevant to management research.
Q: How are these qualitative research methods applied in management research?
A:
- 📉 Exploration: Qualitative methods are used to explore new management topics, phenomena, or research questions, allowing researchers to gain initial insights and generate hypotheses for further investigation.
- 📊 Description: They facilitate the detailed description and documentation of management practices, behaviors, and organizational contexts, providing a rich and nuanced understanding of the phenomena under study.
- 📈 Explanation: Qualitative research methods help explain the underlying reasons, motivations, or mechanisms driving managerial decisions, actions, and outcomes within organizations.
- 💡 Theory Building: These methods contribute to theory building in management research by generating rich empirical data that inform the development of conceptual frameworks, theoretical models, or explanatory constructs.
- 🎯 Evaluation: Qualitative methods are employed to evaluate management interventions, programs, or initiatives, assessing their effectiveness, impact, and implementation processes from multiple stakeholder perspectives.
Q: What are the strengths of using qualitative research methods in management research?
A:
- 📊 Richness of Data: Qualitative methods produce rich, contextually embedded data that capture the complexities and nuances of management phenomena, enhancing understanding and interpretation.
- 📈 Flexibility: These methods offer flexibility in data collection and analysis, allowing researchers to adapt their approaches to suit the dynamic and evolving nature of management research contexts.
- 💡 Exploratory Power: Qualitative research methods are well-suited for exploring new or under-researched management topics, generating novel insights, and stimulating further inquiry.
- 🎯 Holistic Perspective: They provide a holistic perspective on management issues by integrating multiple viewpoints, experiences, and contextual factors into the analysis, leading to comprehensive and nuanced findings.
- 📉 Contextualization: Qualitative methods contextualize management research findings within the specific organizational, cultural, and social contexts in which they occur, enhancing their relevance and applicability to practice.
Q: What are the limitations or challenges associated with using qualitative research methods in management research?
A:
- 📊 Subjectivity: Qualitative research is susceptible to researcher subjectivity and bias, potentially influencing data collection, analysis, and interpretation, and challenging the validity and reliability of findings.
- 📈 Generalizability: Findings from qualitative research may lack generalizability to broader populations or contexts due to the small sample sizes, purposive sampling methods, and context-specific nature of the data.
- 💡 Time and Resource Intensity: Qualitative research can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, requiring extensive data collection, transcription, and analysis, which may limit its feasibility in some management research contexts.
- 🎯 Interpretive Complexity: Qualitative data analysis involves interpretive processes that require researchers to navigate complex layers of meaning, context, and interpretation, which can be challenging and subjective.
- 📉 Integration with Quantitative Data: Integrating qualitative findings with quantitative data in mixed-methods research designs may pose challenges in terms of reconciling divergent findings, synthesizing insights, and maintaining methodological rigor.
In summary, qualitative research methods offer valuable tools for exploring, describing, explaining, and evaluating management phenomena in-depth. While they provide rich and nuanced insights that enhance understanding and theory development in management research, they also present challenges related to subjectivity, generalizability, resource intensity, interpretive complexity, and integration with quantitative data. Researchers must carefully consider these factors when designing and conducting qualitative research in management contexts to maximize the validity, reliability, and relevance of their findings.
-

Qualitative research methodology I qualitative research methods an overview
-

QUALITATIVE Research Design: Everything You Need To Know (With Examples)
-
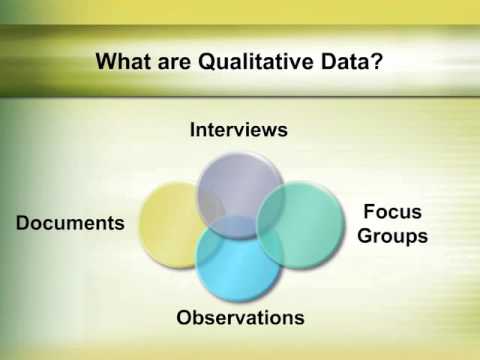
Overview of Qualitative Research Methods
-

Qualitative vs Quantitative vs Mixed Methods Research: How To Choose Research Methodology
-

Fundamentals of Qualitative Research Methods: What is Qualitative Research (Module 1)
-
![Research Methods and Techniques [Video-4]](../vi/YOppeXzFkBs/hqdefault.jpg)
Research Methods and Techniques [Video-4]
