💼 PREFERENCE AS A SOURCE OF FINANCE
Q: What is Preference Financing?
A: Preference financing, also known as preference share financing, refers to the process of raising capital by issuing preference shares to investors in exchange for funds. Preference shares represent a hybrid form of financing that combines features of both debt and equity securities, offering investors preferential rights and priority claims over common shareholders in terms of dividends and liquidation proceeds.
Q: What are the Characteristics of Preference Financing?
A: The characteristics of preference financing include:
- Dividend Priority: Preference shares have preferential dividend rights, entitling shareholders to receive fixed or cumulative dividends before common shareholders, typically at a specified rate or percentage of par value.
- No Voting Rights: Preference shares usually do not carry voting rights in corporate governance matters, such as electing the board of directors or approving major decisions, allowing common shareholders to retain control over the company’s management and strategic direction.
- Priority in Liquidation: Preference shares have priority claims over common shares in the event of liquidation or winding-up of the company, entitling preference shareholders to receive their initial investment back before common shareholders receive any proceeds.
- Convertible Features: Preference shares may include convertible features that allow investors to convert their holdings into common shares at predetermined terms and conditions, providing potential upside and capital appreciation opportunities.
Q: What are the Types of Preference Shares?
A: The types of preference shares include:
- Cumulative Preference Shares: Cumulative preference shares entitle shareholders to accumulate unpaid dividends over time, with any arrears or unpaid dividends accruing and becoming payable in future periods before dividends are paid to common shareholders.
- Non-Cumulative Preference Shares: Non-cumulative preference shares do not accumulate unpaid dividends, meaning that any missed or unpaid dividends in one period are not carried forward or accumulated for future payment, providing flexibility for the company to suspend dividends without incurring obligations.
- Participating Preference Shares: Participating preference shares give shareholders the right to participate in additional dividends or surplus profits after preferred dividends are paid, allowing preference shareholders to share in the company’s earnings growth and value creation alongside common shareholders.
- Convertible Preference Shares: Convertible preference shares can be converted into common shares at the option of the holder or at predetermined conversion terms, providing investors with flexibility and potential upside by participating in the company’s equity appreciation.
Q: What are the Advantages of Preference Financing?
A: The advantages of preference financing include:
- Priority in Dividends: Preference shareholders have priority rights to receive fixed or cumulative dividends before common shareholders, providing income stability and security for investors.
- Priority in Liquidation: Preference shareholders have priority claims over common shareholders in the event of liquidation or winding-up of the company, ensuring capital preservation and downside protection for preference investors.
- No Dilution of Control: Preference financing does not dilute voting control or ownership rights of common shareholders, allowing existing shareholders to retain control over the company’s management and strategic decisions.
- Flexibility in Dividend Policy: Preference financing provides flexibility for the company to tailor dividend policies, payment schedules, and dividend rates to meet the needs of investors and manage cash flow variability.
Q: What are the Disadvantages of Preference Financing?
A: The disadvantages of preference financing include:
- Fixed Dividend Obligations: Preference shares entail fixed or cumulative dividend obligations, requiring the company to make regular dividend payments even in periods of financial difficulty or reduced profitability, which may strain cash flow and financial flexibility.
- Cost of Capital: Preference financing may have a higher cost of capital compared to debt financing or common equity financing, as preference shareholders expect higher dividend rates or preferential treatment in exchange for investing in the company’s capital.
- Limited Upside Potential: Preference shareholders may have limited upside potential compared to common shareholders, as they do not participate in the company’s equity appreciation or growth potential to the same extent, especially if preference shares lack convertible or participating features.
- Complex Capital Structure: Preference financing can result in a complex capital structure with multiple classes of preference shares, each with different rights, preferences, and priorities, which may complicate corporate governance, financial reporting, and investor relations.
Q: How do Companies Issue Preference Financing?
A: Companies issue preference financing by:
- Issuing Preference Shares: Issuing preference shares through private placements or public offerings to investors, institutional investors, or venture capital firms in exchange for funds to finance operations, investments, or growth initiatives.
- Structuring Terms: Structuring the terms and conditions of preference shares, including dividend rates, payment schedules, conversion features, liquidation preferences, and redemption rights, to attract investors and align with the company’s financing objectives.
- Listing on Stock Exchanges: Listing preference shares on stock exchanges or capital markets to enhance liquidity, visibility, and marketability for investors seeking to buy or sell preference shares in the secondary market.
- Complying with Regulatory Requirements: Complying with regulatory requirements, disclosure obligations, and corporate governance standards imposed by securities regulators, stock exchanges, or financial authorities when issuing preference shares to ensure transparency and investor protection.
Q: How do Companies Utilize Preference Financing?
A: Companies utilize preference financing by:
- Funding Growth Initiatives: Using preference financing to fund organic growth initiatives, expansion projects, acquisitions, or strategic investments that enhance the company’s market position, product offerings, or geographic reach.
- Managing Capital Structure: Managing the company’s capital structure by balancing debt, equity, and preference financing to optimize financing costs, leverage ratios, and weighted average cost of capital (WACC) while maintaining financial flexibility and risk management.
- Supporting Working Capital Needs: Utilizing preference financing to support working capital needs, finance inventory purchases, fund accounts receivable, or manage cash flow fluctuations associated with operating activities.
- Refinancing Debt: Using preference financing proceeds to refinance existing debt obligations, retire high-cost debt, or extend debt maturities to improve the company’s financial flexibility, debt service capacity, and cost of capital.
Q: How do Companies Manage Preference Financing Risks?
A: Companies manage preference financing risks by:
- Maintaining Dividend Stability: Maintaining dividend stability, consistency, and predictability for preference shareholders by managing cash flow, profitability, and financial performance to meet dividend obligations and avoid dividend defaults.
- Monitoring Capital Structure: Monitoring the company’s capital structure, leverage ratios, and financial health to ensure the sustainable use of preference financing and prevent overreliance on preferred shares that may strain financial resources or impact creditworthiness.
- Communicating with Investors: Communicating openly and transparently with preference shareholders through regular financial reporting, investor updates, and dividend announcements to build trust, manage expectations, and maintain investor confidence in the company’s performance and financial condition.
- Analyzing Redemption Risks: Analyzing redemption risks, call provisions, and redemption rights associated with preference shares to assess potential redemption scenarios, manage liquidity needs, and mitigate refinancing risks for preference financing in the future.
📈 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, preference financing is a versatile source of funding for companies to raise capital and finance their operations, investments, and growth initiatives. By understanding the characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and implications of preference financing, companies can make informed decisions, manage financing risks effectively, and optimize their capital structure to create long-term value for shareholders.
Keywords: Preference Financing, Preference Shares, Dividend Priority, Capital Structure.
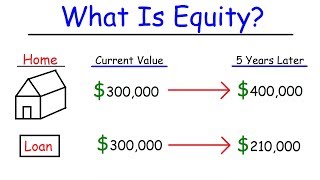
What is Equity Financing ? | Simplified