💼 EQUITY AS A SOURCE OF FINANCE
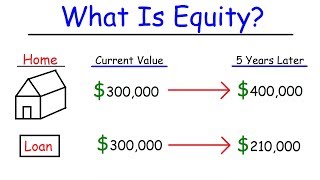
Q: What is Equity Financing?
A: Equity financing refers to the process of raising capital by issuing ownership shares in the company to investors in exchange for funds. Equity financing provides companies with external funds without incurring debt obligations and involves sharing ownership rights, dividends, and voting control with shareholders.
Q: What are the Characteristics of Equity Financing?
A: The characteristics of equity financing include:
- Ownership Stake: Equity financing involves issuing ownership shares, such as common stock or preferred stock, to investors who become shareholders and partial owners of the company.
- Dividend Payments: Equity financing may involve paying dividends to shareholders as a distribution of profits or earnings, although companies are not obligated to pay dividends if profits are reinvested.
- Voting Rights: Equity financing grants shareholders voting rights in corporate governance matters, such as electing the board of directors, approving major decisions, or voting on strategic initiatives.
- No Repayment Obligation: Equity financing does not require repayment of the funds raised, as shareholders invest in the company with the expectation of sharing in its profits and growth potential.
Q: What are the Advantages of Equity Financing?
A: The advantages of equity financing include:
- No Repayment Obligation: Equity financing does not involve repayment obligations or interest payments, providing flexibility and reducing financial risk for the company.
- Permanent Capital: Equity financing provides permanent capital to the company, as equity investors do not expect repayment of their investment and share in the company’s profits and growth potential indefinitely.
- Risk Sharing: Equity financing allows companies to share financial risks and rewards with investors, aligning incentives and fostering long-term partnerships with shareholders.
- No Fixed Payments: Equity financing does not involve fixed payments or interest costs, preserving cash flow and financial flexibility for the company to pursue growth opportunities and strategic initiatives.
Q: What are the Disadvantages of Equity Financing?
A: The disadvantages of equity financing include:
- Ownership Dilution: Equity financing involves issuing ownership stakes in the company to investors, diluting existing shareholders’ ownership rights and control over the company’s management and decision-making.
- Dividend Obligations: Equity financing requires companies to pay dividends to shareholders, reducing retained earnings available for reinvestment in the business and limiting financial flexibility.
- Market Volatility: Equity financing exposes companies to market volatility, stock price fluctuations, and investor sentiment, impacting shareholder value and market capitalization over time.
- Information Disclosure: Equity financing may require companies to disclose sensitive information, financial statements, and strategic plans to investors, analysts, and regulatory authorities, compromising confidentiality and competitive advantage.
Q: What are the Types of Equity Financing?
A: The types of equity financing include:
- Common Stock: Issuing common stock to investors in exchange for ownership rights, voting control, and participation in the company’s profits through dividends and capital appreciation.
- Preferred Stock: Issuing preferred stock to investors with preferential rights, such as priority dividend payments, liquidation preferences, and convertible features, in exchange for equity ownership.
- Convertible Securities: Issuing convertible securities, such as convertible bonds, convertible preferred stock, or convertible notes, that allow investors to convert their holdings into common stock at predetermined terms and conditions.
- Equity Crowdfunding: Raising capital from a large number of individual investors or crowdfunding platforms through online platforms or social networks in exchange for equity stakes in the company.
Q: How do Companies Determine the Valuation of Equity Financing?
A: Companies determine the valuation of equity financing by:
- Assessing Market Conditions: Assessing prevailing market conditions, investor sentiment, industry trends, and comparable company valuations to gauge the company’s market value and pricing expectations.
- Performing Financial Analysis: Performing financial analysis, discounted cash flow (DCF) modeling, and valuation techniques, such as comparable company analysis (CCA) or precedent transactions analysis (PTA), to estimate the company’s intrinsic value and equity worth.
- Engaging in Negotiations: Engaging in negotiations with investors, investment bankers, or valuation experts to establish a fair valuation and pricing for the company’s equity securities based on demand, supply, and market dynamics.
- Considering Growth Prospects: Considering the company’s growth prospects, earnings potential, competitive advantage, and industry positioning to justify the valuation and attractiveness of equity financing opportunities to investors.
Q: How do Companies Issue Equity Financing?
A: Companies issue equity financing by:
- Initial Public Offering (IPO): Conducting an initial public offering (IPO) to offer shares of common stock to the public markets for the first time, enabling investors to purchase ownership stakes in the company.
- Follow-On Offerings: Conducting follow-on offerings or secondary offerings to issue additional shares of common stock to existing shareholders or new investors to raise additional equity capital for the company.
- Private Placements: Conducting private placements or direct placements of equity securities to institutional investors, accredited investors, or venture capital firms in private transactions outside the public markets.
- Equity Crowdfunding: Conducting equity crowdfunding campaigns through online platforms or crowdfunding portals to raise capital from a broad base of individual investors or retail investors in exchange for equity stakes in the company.
Q: How do Companies Utilize Equity Financing?
A: Companies utilize equity financing by:
- Funding Growth Initiatives: Using equity financing to fund organic growth initiatives, expansion projects, research and development (R&D) activities, or strategic acquisitions that enhance the company’s market position and competitiveness.
- Supporting Working Capital Needs: Utilizing equity financing to support working capital needs, finance inventory purchases, fund accounts receivable, or manage cash flow fluctuations associated with operating activities.
- Investing in CapEx: Investing in capital expenditures (CapEx), infrastructure upgrades, or technology investments that improve operational efficiency, productivity, and long-term sustainability of the business.
- Paying Down Debt: Using equity financing proceeds to repay existing debt obligations, refinance high-cost debt, or reduce leverage levels to improve the company’s financial stability, creditworthiness, and cost of capital.
Q: How do Companies Manage Equity Financing Risks?
A: Companies manage equity financing risks by:
- Maintaining Shareholder Relations: Maintaining open communication, transparency, and trust with shareholders through regular financial reporting, investor updates, and corporate governance practices to mitigate investor concerns and preserve shareholder value.
- Aligning Interests: Aligning the interests of management, employees, and shareholders through equity ownership, incentive compensation, stock options, or performance-based rewards to promote accountability, alignment, and long-term value creation.
- Managing Dilution: Managing dilution effects of equity financing on existing shareholders by implementing anti-dilution provisions, share repurchase programs, or stock buybacks to offset dilution impact and preserve shareholder value.
- Monitoring Market Conditions: Monitoring market conditions, investor sentiment, and stock price performance to anticipate changes in equity valuations, market trends, and investor preferences that may affect the company’s equity financing strategy and timing.
📈 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, equity financing is a fundamental source of funding for companies to raise capital and finance their operations, investments, and growth initiatives. By understanding the characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and implications of equity financing, companies can make informed decisions, manage financing risks effectively, and optimize their capital structure to create long-term value for shareholders.
Keywords: Equity Financing, Ownership Stakes, Dividend Payments, Valuation, Capital Structure.
What is Equity Financing ? | Simplified